Chronic and acute IBD mouse models for preclinical research
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract, among which the most prominent ones are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, affecting millions of people worldwide. Large numbers of preclinical candidates have been evaluated, but few have reached the clinic, and even fewer have reached the market. Robust preclinical IBD mouse models are essential to mimic disease mechanisms, evaluate therapeutic efficacy, and accelerate drug development.
Oncodesign Services offers a broad portfolio of IBD, Crohn’s, and colitis mouse models, including acute and chronic models, and provides de novo development of new IBD models to support your research from early discovery to translational validation.
Whether you’re evaluating novel biologics, anti-inflammatory small molecules, or immune-modulating strategies, our in vivo and in vitro IBD models provide the translational bridge between discovery and clinical development.
Selecting endometriosis mouse models for preclinical studies
Examples of available in vivo IBD models*
- Acute DSS induced colitis model in mice and rats
- DSS + anti-CLA4 antibody induced chronic colitis model (exclusive to Oncodesign Services)
- Acute TNBS colitis model
- Anti-CD40 antibody-induced colitis model
- IL-10 knockout colitis mouse model
- Chronic DSS colitis model
- AOM-DSS-induced colitis-associated cancer model
- T-cell transfer model of colitis
*Models are available in WT mice, custom transgenic mice (e.g. humanised for specific targets), and human CD34+ reconstituted mice.
Oncodesign Services can also develop custom-made models to support specific scientific needs where required.
Confirm model suitability before study initiation: To support confident model selection, histology samples from established endometriosis research models can be accessed ahead of full study commitment. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) or FISH analyses may be performed to assess target expression and tissue localization, helping confirm biological relevance before program initiation.
Key readouts and biomarkers
- Clinical Scoring: Daily “Disease Activity Index (DAI)” (weight loss, stool consistency, blood in stool, colon length).
- Tissue Analysis: H&E and Alcian Blue-PAS-stained colon sections for assessing epithelial erosion and healing, crypt architecture and goblet cell depletion.
- Molecular Profiling: qRT-PCT/dPCR for key inflammatory mediators (TNFα, IL1β, IL6, CXCL10 etc) or other relevant genes (e.g. drug target), IHC, and cytokine multiplex assays (e.g. IL17A/F, IFNγ etc.).
- Cellular & Biomarker Readouts: Flow cytometry for profiling immune infiltrates (Th1, Th17, Tregs, neutrophils, monocytes etc.), human cell subsets in HIS mice (hCD45+, hCD4+, hCD8+), serum and faecal biomarker quantification (calprotectin, LCN-2 etc.) and PK/PD assessment when applicable.
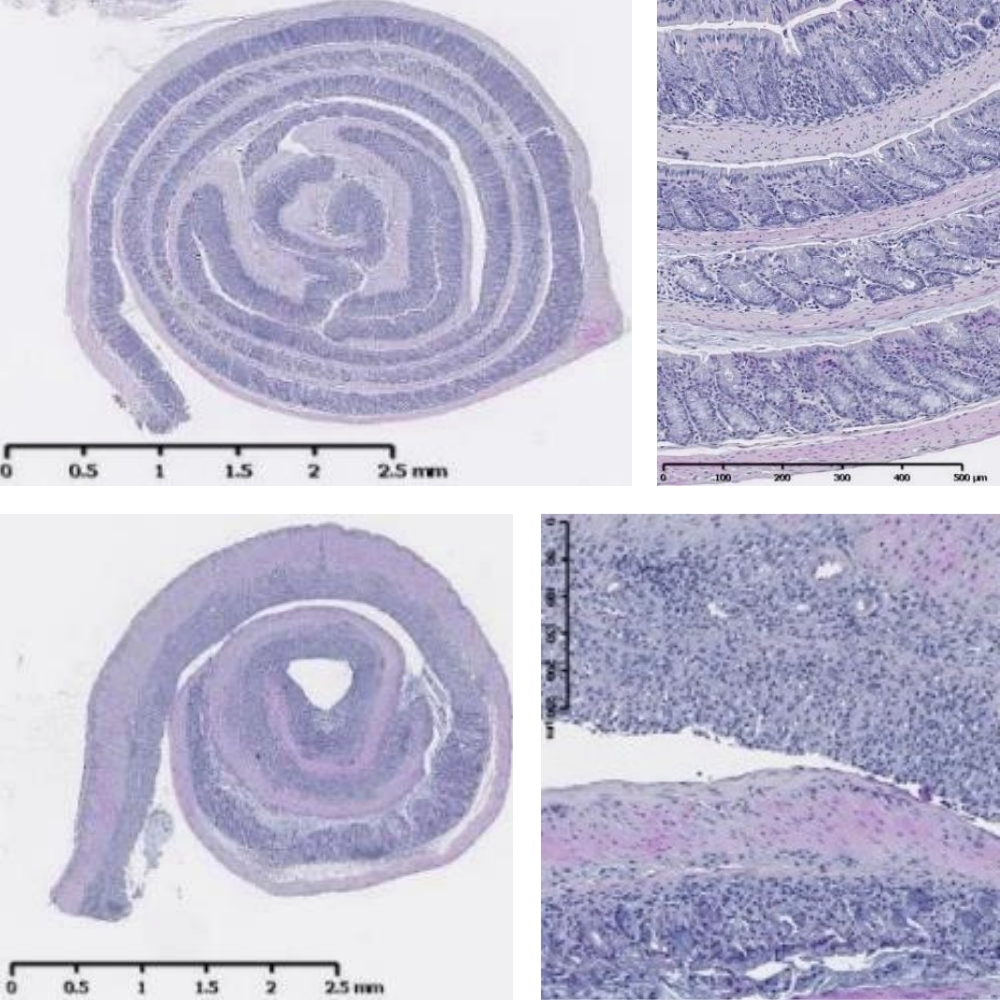
H&P stain slides of IBD model tissue samples. Top: Colon of animals receiving water (negative controls). Bottom: Colon of animals receiving 2% DSS.
Selection of IBD mouse model case studies
At Oncodesign Services, we do more than provide preclinical models. We help you select the best model to support your research objective, adapt it to your project, and generate meaningful data that drive decisions. Whether you’re exploring a new mechanism or advancing a lead candidate, our team is here to support you at every step.
-
DSS-induced acute colitis
DSS-induced acute colitis
DSS is added to drinking water, over a 5-day treatment protocol. Tacrolimus (FK-506 immuno-suppressor) partially limits the evolution of the disease, as seen by improved DAI. Untreated animals display increased spleen size and weight at D7, and colon shortening.
Tacrolimus limits spleen inflammatory cell accumulation. Cytokine expression can be measured by qRT-PCR, and a classic inflammatory profile is typically observed, with elevated IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-6.
Score Body weight loss (%) Stool consistency Blood in faeces 0 0 Normal Absence 1 1-5 Soft Hemoccult + 2 6-10 Very soft Hemoccult ++ 3 11-15 Diarrhoea Bloody 4 >15 Severe diarrhoea 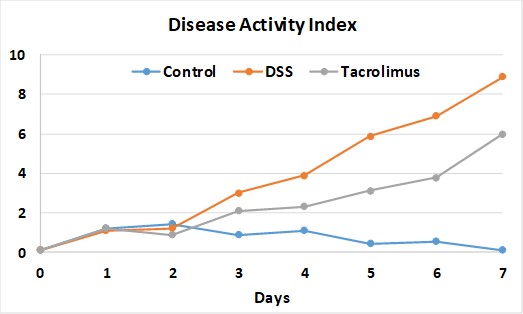
Above: Kinetics of disease activity index (DAI) in the acute DSS model.
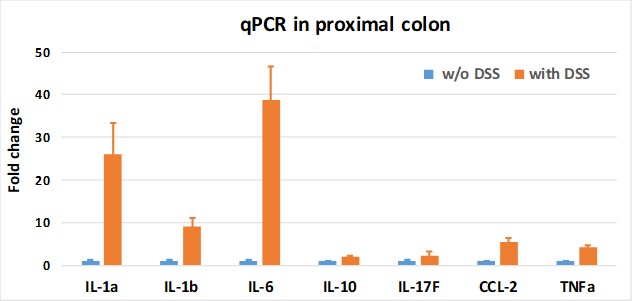
Above: qRT-PCR measurement of fold change of expression of genes of interest in the acute DSS colitis mouse model.
-
DSS-induced colitis chroncized by anti-CTLA4 antibody administration
DSS-induced colitis chroncized by anti-CTLA4 antibody administration
Immuno-oncology approaches are promising new cancer treatments, but a number of unfortunate side effects need to be managed clinically. These typically result from hyper-activation of the immune system, which can affect the gut, skin, liver or endocrine glands. Over 1/3 of patients receiving the anti-CTLA4 antibody Ipilimunab report colitis symptoms, for example.
Oncodesign Services has developed a model in which this side-effect is used to create a chronic colitis model, by combining the antibody with DSS as a standard colitis inducer. Mice typically recover from the DSS-induced colitis after DSS removal on D6, but anti-CTLA4 treatment delays the recovery phase, mimicking chronic colitis and allowing for the evaluation of compounds aiming at decreasing recovery time after an IBD crisis.
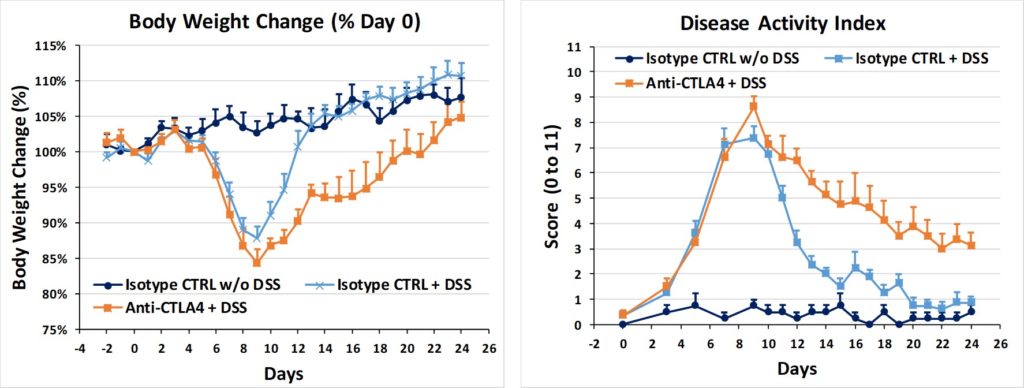
Left: Kinetics of body weight loss (relative to D0 of the procedure) in the acute DSS model vs the chronicized DSS + antiCTLA4 antibody model.
Right: Kinetics of disease activity index (DAI) in the acute DSS model vs the chronicized DSS + anti-CTLA4 antibody model.
Learn more about our inflammatory bowel disease models
Oncodesign Services offers CRO services for preclinical models addressing a variety of inflammatory, fibrotic and auto-immune pathologies, and provides support for de novo development of new models. Our highly experienced inflammation team can work with you to select models and design studies with the translational relevance required to underpin strong funding applications and advance confidently to the clinic.
Talk to our team today to find out more about the models and services available to support your IBD research, learn how we partner with research teams creating innovative therapies for inflammatory diseases, and to request a quote:
Frequently asked questions about our IBD mouse models:
Can Oncodesign Services help me select the best model for my program?
Oncodesign Services works closely with you to help select the most appropriate model(s) for your study.
Our scientific experts take the time to understand your research objectives, target biology, therapeutic modality, and stage of development. Based on this, we recommend models that are best suited to answer your specific scientific questions, whether that involves in vitro systems, in vivo models, or more advanced translational approaches. When needed, we also discuss the strengths, limitations, and alternatives of each option so you can make an informed decision with confidence.
Our goal is to ensure your chosen IBD model is scientifically relevant, robust, and aligned with your project timelines and decision-making needs.
Is it possible to make a decision on ex vivo analyses after reviewing DAI results?
Yes. We are flexible and can adapt the study design to help you manage timelines and budgets efficiently.
You may choose to wait until the DAI results are available before deciding whether to proceed with ex vivo analyses. This staged approach allows you to limit upfront costs and make data-driven decisions as the study progresses. At the same time, it’s important to note that ex vivo analyses such as histology and qRT-PCR can be highly informative, particularly when DAI results are not as expected. These analyses can help elucidate why a compound did not demonstrate the desired effect by providing mechanistic and biological context.
We work with you to balance scientific insight and budget considerations, ensuring the level of analysis aligns with your objectives and decision-making strategy.
Do I need an acute or chronic IBD mouse model?
The choice between acute and chronic IBD models depends on the specific scientific questions you need to answer. Acute models are typically used in early-stage studies to rapidly assess anti-inflammatory activity and establish proof of concept under controlled conditions. Chronic models, by contrast, are better suited for evaluating durability of response, relapse, longer-term safety, and clinically relevant dosing strategies over time. Neither approach is inherently more realistic; each is designed to interrogate different aspects of disease biology and treatment response.
Our inflammatory disease specialists will work closely with you to align model selection with your therapeutic mechanism, development stage, and translational objectives, ensuring your study generates meaningful data.
You can learn more about the acute vs chronic decision-making process in this short article.