

Seeking Pharmacology Support for your Fibrosis Programs?
Fibrosis is an extremely complex process that depends on the interactions of many cells, molecules and different pathways. Animal models are valuable means to examine the pathogenesis of these diseases, to identify potential therapeutic targets and develop novel therapies for various fibrotic diseases. At Oncodesign Services, we offer and develop various models of fibrotic diseases including NASH liver diseases for pharmacology studies.
Fibrosis, a disease with high unmet medical needs
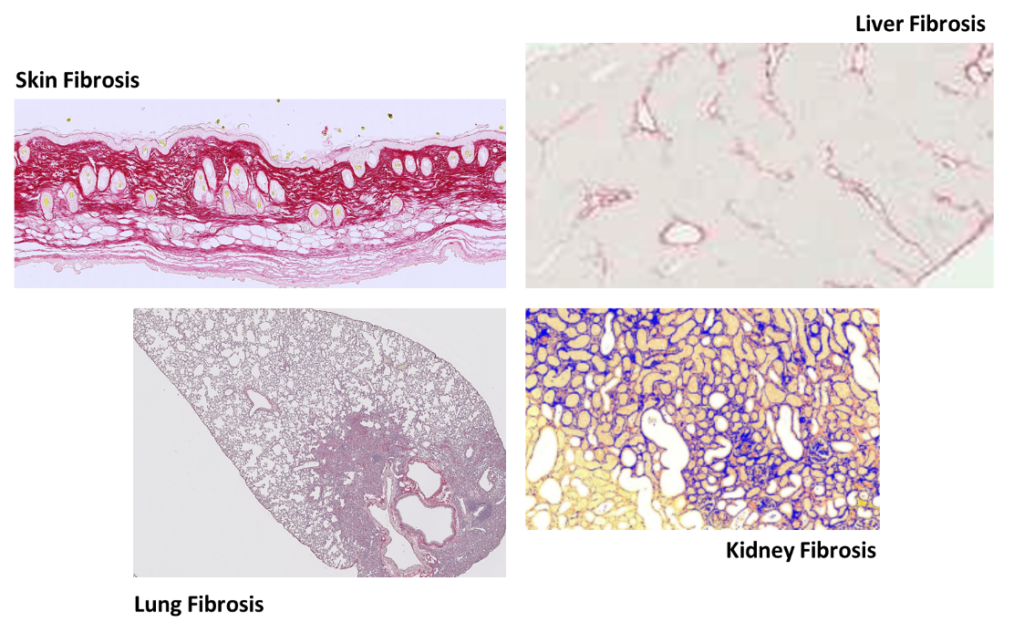
Fibrosis is characterized by excessive formation and deposition of fibrous connective tissue (scarring) resulting in progressive architectural remodeling in tissues and organs. Fibrotic disorders, such as NASH, liver sclerosis, pulmonary fibrosis, scleroderma, renal interstitial fibrosis, sequelae to myocardial infarction, systemic sclerosis, and side effects of graft-versus host-disease (GVHD), result in loss of function of affected organs and have been estimated to contribute to approximately 45% of all-cause mortality in the United States. There are no currently approved treatments for fibrosis.
The fibrosis cascade is typically initiated by inflammatory insult, resulting in upregulation of TGF-beta, which recruits macrophages that secrete metalloproteases (MMPs) that degrade the extracellular matrix (ECM) to remodel the tissue. This triggers differentiation and activation of myofibroblasts that deposit collagen fibers to cause scarring and organ stiffness.
Oncodesign Services Fibrosis models to support your drug development
Fibrosis models constitute an essential tool for preclinical research, allowing to study the development of fibrosis, replicate the fibrosis-related diseases observed in human patients and develop new therapies.
Oncodesign Services offers stable models, tight data and responsive business culture to support your fibrosis programs. Validated mouse fibrosis models include:
- Respiratory fibrosis: bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis
- Skin fibrosis: bleomycin-induced scleroderma, Topoisomerase-l immunization-induced skin fibrosis
- Liver fibrosis: CCl4-induced fibrosis, Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Kidney fibrosis: Unilateral ureteral ostruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis
To supplement clinical readouts (body weight and clinical scoring) a number of biomarker readouts can be obtained by histology, IHC, ELISA, MSD, Bio-Plex PCR/RT-q-PCR, and flow/FACS. Read more about our bioanalytical platform here.
-
Lung fibrosis models
Lung fibrosis is estimated to affect more than 5 per 100,000 people per year in the USA and Europe. It can lead to chronic respiratory insufficiency and limited treatment options are available to those suffering from it.
At Oncodesign Services, we have deep experience with administration formats of the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis models, i.e. by intratracheal and by subcutaneous mini-pumps. These administration routes result in different patterns of lesions, time-courses of disease induction and different cohort consistency.
Readouts include clinical scoring of animal health, lung imaging (CT-scan), histology, lung functionality and gene expression. Combining a variety of readouts allows us to provide robust preclinical models of lung fibrosis. Oncodesign Services has implemented and validated the flexiVent® system (Scireq™). This system provides clinically relevant readouts of lung function. This approach allows to evaluate the efficacy of our client’s candidate drugs along all relevant dimensions of the disease.
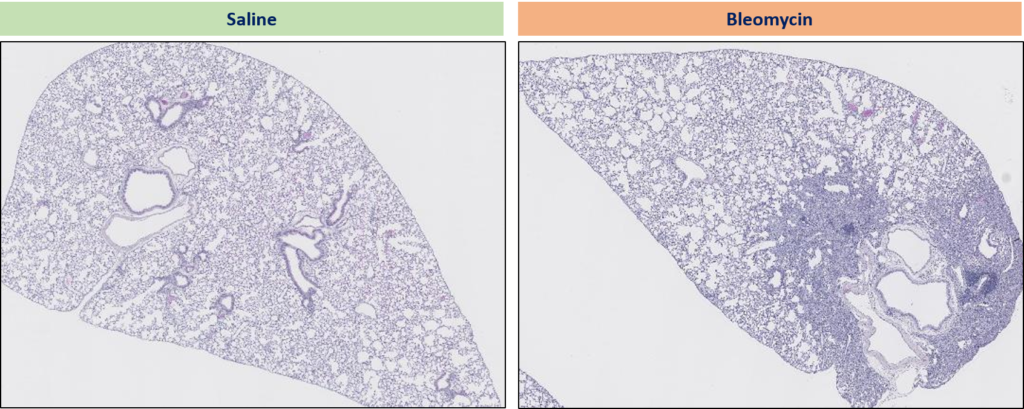
Bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice : Lung histology at Day 21
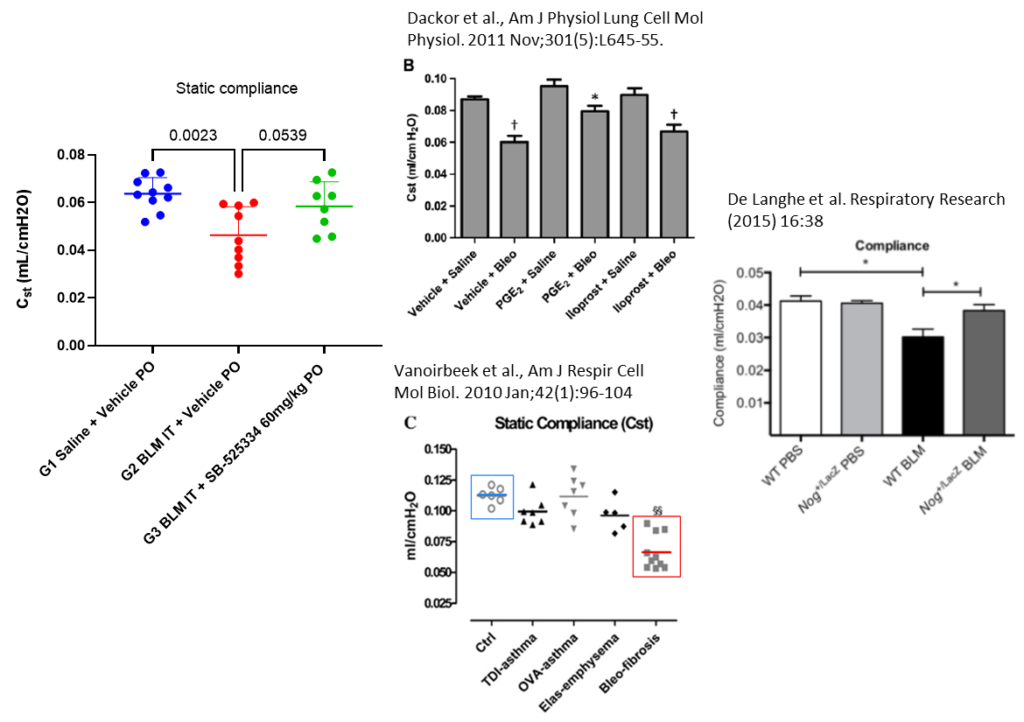
Flexivent analysis of lung mechanics in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model in C57BL/6 mice : Compliance improvement with SB-52334
-
Skin fibrosis (Scleroderma) models
The bleomycin-induced scleroderma model is widely used in academia and industry. Mice are given daily subcutaneous injections of bleomycin for 6 weeks. The main readouts include clinical follow-up of body weight loss and signs of skin inflammation followed by hardening, histological quantifications of collagen deposition in the skin and the lungs, skin thickening. Additionally, skin gene expression (qRT-PCR) can be performed to follow the kinetics of cytokine induction.
-
Liver fibrosis models
The CCl4 model of liver fibrosis is a classical model widely used in preclinical drug testing. Mice are given repeated doses of CCl4. Liver fibrosis then typically appears after 6 weeks. This model is useful for testing therapies aiming to modulate collagen deposition and expression of metalloproteases. ALK5 (TGFb receptor I) inhibitors, exploiting a well-known anti-fibrotic mechanism, decrease collagen production and are used as a reference therapy.
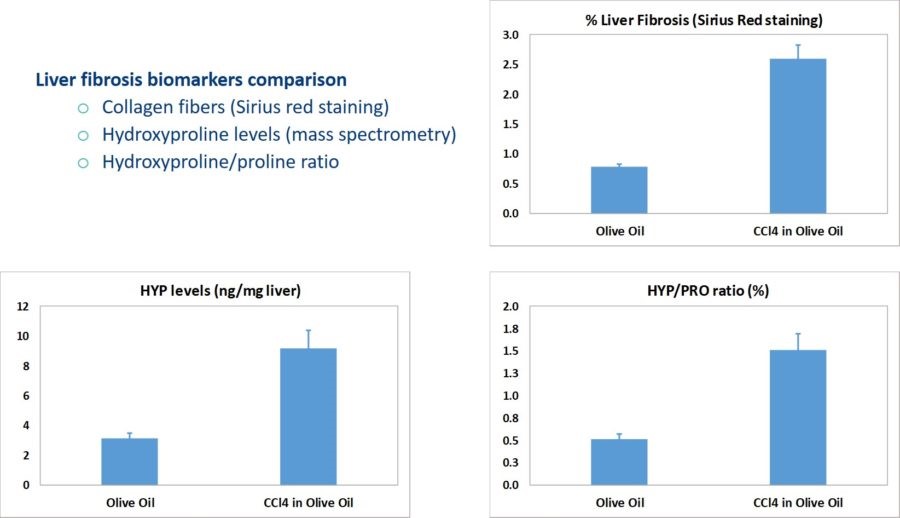
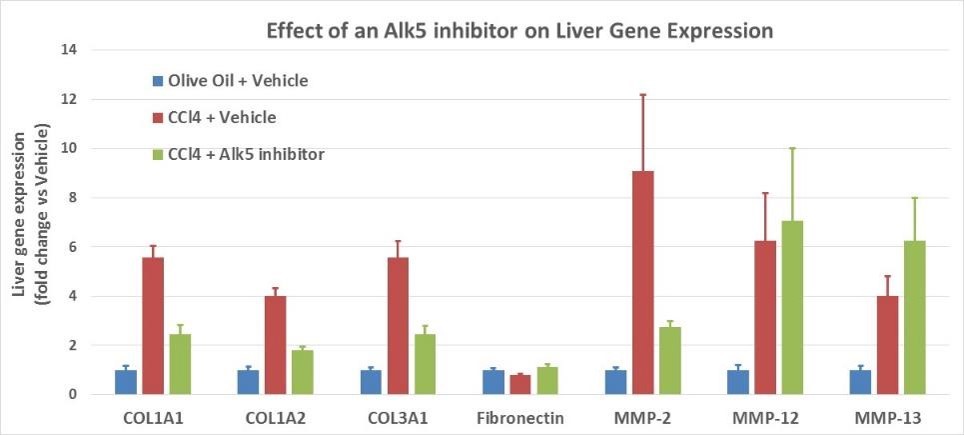
-
NASH models
NASH, for Non-Alcoholic SteatoHepatitis, is a chronic liver disease that can lead to fibrosis and Hepato-Cellular Carcinoma (HCC). It is a major cause of liver disease in developed countries (around 20 million in US suffer from NASH & advanced fibrosis), with estimated prevalence of 24% of general population, with an increase of HCC incidence by 3% annually in the past 10 years.
Example of NASH components
- Presence of steatosis (abnormal intracellular retention of lipids) and inflammation
- Inflammatory infiltrates
- Hepatocyte injury (hepatocyte ballooning and cell death)
- Progressive fibrosis (collagen fiber deposition)
In preclinical research, NASH models allow testing of new potential treatments before clinical trials.
Oncodesign Services provides a large portfolio of in vitro and in vivo models ininflammation diseases, including Chronic liver injury models in mice such as:
Carbon Tetrachloride & high fat diet-induced NASH model in mice
- STZ+HFD NASH
- CCl4+HFD NASH
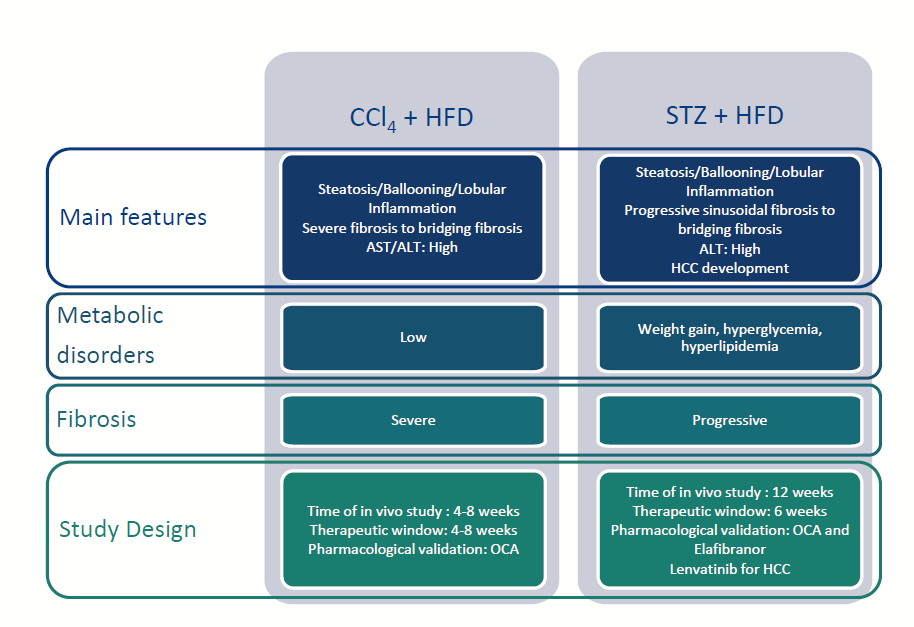
Streptozotocin & high fat diet-induced NASH model in mice
- Long term NASH-HCC
-
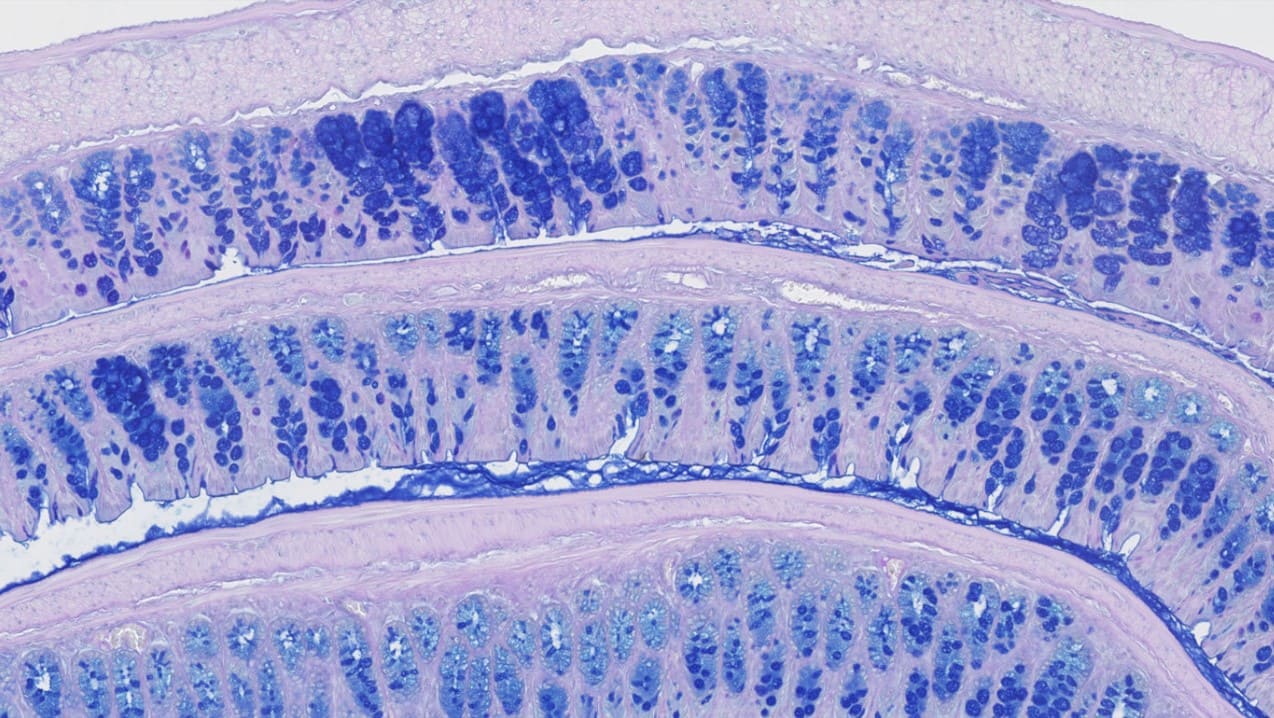
Kidney fibrosis models
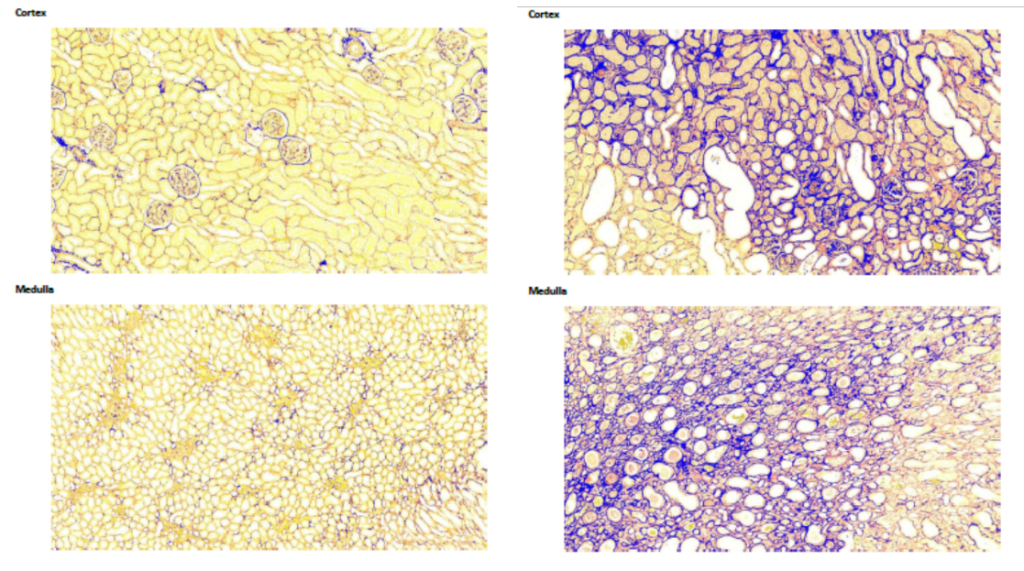
Oncodesign Services offers Kidney fibrosis model in rats, induced by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction (UUO)
Kidney fibrosis induced by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction (UUO)
Case study: Animal models for novel therapies on fibrosis and NASH: Pharmacological validation and gender differences.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD) represent a spectrum of chronic liver disease ranging from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, and then liver fibrosis or liver cirrhosis. NAFLD are strongly associated with metabolic syndrome including obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), dyslipidemia and hypertension.
Sex differences exist in the prevalence, risk factors, fibrosis and clinical outcomes of NAFLD suggesting that a proper consideration of sex, age and hormonal differences are needed to fill current gaps and implement precision medicine for patients with NAFLD.
In this case, we have used a model of NASH with number of cellular and molecular processes that are reflective of human NASH and outcomes. Our objective was to assess:
- The effect of Elafibranor or/and Obeticholic Acid on the development of NASH and fibrosis.
- The effect of Lenvatinib or/and anti-PD-1 on the development of HepatoCellular Carcinomas (HCC)
- To assess the sex difference on the pathogenesis and the response to treatments.
Also to discover
Contact us for more information



